Decomposition method (constraint satisfaction)
In constraint satisfaction, a decomposition method translates a constraint satisfaction problem into another constraint satisfaction problem that is binary and acyclic. Decomposition methods work by grouping variables into sets, and solving a subproblem for each set. These translations are done because solving binary acyclic problems is a tractable problem.
Each structural restriction defined a measure of complexity of solving the problem after conversion; this measure is called width. Fixing a maximal allowed width is a way for identifying a subclass of constraint satisfaction problems. Solving problems in this class is polynomial for most decompositions; if this holds for a decomposition, the class of fixed-width problems form a tractable subclass of constraint satisfaction problems.
Contents |
Overview
Decomposition methods translate a problem into a new one that is easier to solve. The new problem only contains binary constraints; their scopes form a directed acyclic graph. The variables of the new problem represent each a set of variables of the original one. These sets are not necessarily disjoint, but they cover the set of the original variables. The translation finds all partial solutions relative to each set of variables. The problem that results from the translation represents the interactions between these local solutions.
By definition, a decomposition method produces a binary acyclic problem; such problems can be solved in time polynomial in its size. As a result, the original problem can be solved by first translating it and then solving the resulting problem; however, this algorithm is polynomial-time only if the decomposition does not increase size superpolynomially. The width of a decomposition method is a measure of the size of problem it produced. Originally, the width was defined as the maximal cardinality of the sets of original variables; one method, the hypertree decomposition, uses a different measure. Either way, the width of a decomposition is defined so that decompositions of size bounded by a constant do not produce excessively large problems. Instances having a decomposition of fixed width can be translated by decomposition into instances of size bounded by a polynomial in the size of the original instance.
The width of a problem is the width of its minimal-width decomposition. While decompositions of fixed width can be used to efficiently solve a problem, a bound on the width of instances does necessarily produce a tractable structural restriction. Indeed, a fixed width problem has a decomposition of fixed width, but finding it may not be polynomial. In order for a problem of fixed width being efficiently solved by decomposition, one of its decompositions of low width has to be found efficiently. For this reason, decomposition methods and their associated width are defined in such a way not only solving the problem given a fixed-width decomposition of it is polynomial-time, but also finding a fixed width decomposition of a fixed-width problem is polynomial-time.
Decomposition methods
Decomposition methods create a problem that is easy to solve from an arbitrary one. Each variable of this new problem is associated to a set of original variables; its domain contains tuples of values for the variables in the associated set; in particular, these are the tuples that satisfy a set of constraints over these variables. The constraints of the new problem bounds the values of two new variables to have as values two tuples that agree on the shared original variables. Three further conditions ensure that the new problem is equivalent to the old one and can be solved efficiently.
In order for the new problem to be solvable efficiently, the primal graph of the new problem is required to be acyclic. In other words, viewing the variables as vertices and the (binary) constraints as edges, the resulting graph is required to be a tree or a forest.
In order for the new problem to be equivalent to the old one, each original constraint is enforced as part of the definition of the domain of at least one new variables. This requires that, for each constraint of the old problem, there exists a variable of the new problem such that its associated set of original variables include the scope of the constraint, and all tuples in its domain satisfy the constraint.
A further condition that is necessary to ensure equivalence is that the binary constraints are sufficient to enforce all "copies" of each original variable to assume the same value. Since the same original variable can be associated to several of the new variables, the values of these new variable must all agree on the value of the old variable. The binary constraints are used to enforce equality of the old variables shared between the two new variables. Two copies of a new variable are forced equal if there exists a path of binary constraints between their new variables and all new variables in this path contain the old variable.
| An example constraint satisfaction problem; this problem is binary, and the constraints are represented by edges of this graph. | |
| A decomposition tree; for every edge of the original graph, there is a node that contains both its endpoints; all nodes containing a variable are connected | |
Solving a subproblem. This example shows solving the subproblem made of all constraints on the variables of the first set 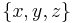 . A similar procedure is done for the other sets . A similar procedure is done for the other sets 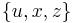 and and 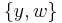 |
|
Each node of the tree is made a variable. Its domain is the set of solutions of the partial problem, which is a set of tuples. The constraints of the new problem allow only the tuples that contain equal values of the original variables. In the figure, equality of 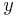 is shown: the corresponding constraint is only met by the first tuple of is shown: the corresponding constraint is only met by the first tuple of 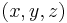 and the first tuple of and the first tuple of 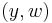 , and by the second tuple of , and by the second tuple of 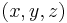 and the second tuple of and the second tuple of 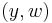 . . |
A decomposition method is usually defined by providing a tree whose nodes are the variables of the new problem; for each node, also provided are the associated set of original variables and possibly a set of original constraints used to build the domain of the variable in the new problem. Of the above three conditions (tree structure, enforcement of constraints, and equivalence of copies of original variables), the first one is automatically enforced by this definition. The condition of enforcement of constraints is in mostly formulated as: the scope of each constraint is a subset of the variables of some node; however, a different condition may be used when nodes are also associated to sets of constraints. The equivalence of all copies of the original variables is usually formulated as: the subgraph induced by the nodes associated to an original variable is connected.
Decomposition methods for binary problems
A number of decomposition methods exist. Most of them generate a tractable class by bounding the width of instances. The following are the decomposition methods defined for binary constraint satisfaction problems. Since a problem can be made binary by translating it into its dual problem or using hidden variables, these methods can be indirectly used to provide a tree decomposition for arbitrary constraint satisfaction problems.
Biconnected components
In graph theory, a separating vertex is a node of a graph that "breaks" the graph when removed from it. Formally, it is a node whose removal from the graph increases the number of its connected components. A biconnected component of a graph is a maximal set of its nodes whose induced subgraph is connected and does not have any separating vertex. It is known from graph theory that the biconnected components and the separating vertices of a graph form a tree. This tree can be built as follows: its nodes are the biconnected components and the separating vertices of the graph; edges only connect a biconnected component with a separating vertex, and in particular this happens if the vertex is contained in the component. It can be proved that this graph is actually a tree.
If the constraints of a binary constraint satisfaction problem are viewed as edges of a graph whose nodes are the variables, this tree is a decomposition of the problem. The width of a decomposition is the maximal number of vertices in a biconnected component.
| The primal graph of a constraint satisfaction problem (every node represents a variable and every edge a constraint between two variables) | Its biconnected components (colored) and its separating vertices (black, only one in this case) | The biconnected decomposition: nodes of the tree are separating vertices and biconnected components |
Cycle cutset
The cycle decomposition method split a problem into a cyclic and an acyclic part. While it does not fit in the definition of the other decomposition methods, which produce a tree whose nodes are labeled with sets of nodes, it can be easily reformulated in such terms.
This decomposition method is based on the idea that, after some variables are given a value, what remains of the problem once these variables have been eliminated may be acyclic. Formally, a cycle cutset of a graph is a set of nodes that makes the graph acyclic when they are removed from it. A similar definition can be given for a constraint satisfaction problem using its primal graph. The width of a cycle decomposition is the number of variables in the cutset. The width of a problem is the minimal width of its cycle cutset decompositions.
| A graph representation of a constraint satisfaction problem | A cycle cutset of the graph (others exist) | Removing the cycle cutset, what remains is an acyclic graph (a tree, in this case, but a forest in general) |
Such a decomposition does not fit in the scheme of the other decompositions because the result of the decomposition is not a tree, but rather a set of variables (those of the cutset) and a tree (formed by the variables not in the cutset). However, a tree like those generated by the other decomposition methods can be obtained from the tree that results from removing the cutset; this is done by choosing a root, adding all variables of the cutset to all its nodes, and the variables of each node to all its children. This results in a tree whose maximal number of variables associated with a node is equal to the size of the cutset plus two. Apart from the addition of two, this is the width of the decomposition, which is defined as the number of variables in the considered cutset.
Tree decomposition
Tree decomposition is a well-known concept from graph theory. Reformulated in terms of binary constraints, a tree decomposition is a tree whose nodes are associated to sets of variables; the scope of each constraint is contained in set of variables of some node, and the subtree of nodes associated to each variable is connected. This is the most general form of decomposition for binary constraints that follows the scheme outlined above, as the conditions imposed on the tree are only the ones that are necessary to guarantee equivalent of the original and new problem.
The width of such a decomposition is the maximal number of variables associated to the same node minus one. The treewidth of a problem is the minimal width of its tree decompositions.
Bucket elimination can be reformulated as an algorithm working on a particular tree decomposition. In particular, given an ordering of the variables, every variable is associated a bucket containing all constraints such that the variable is the greatest in their scope. Bucket elimination corresponds to the tree decomposition that has a node for each bucket. This node is associated all of its constraints, and corresponds to the set of all variables of these constraints. The parent of a node associated to the bucket of 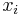 is the node associated to the bucket of
is the node associated to the bucket of 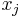 , where
, where 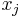 is the greatest node that is in a constraint with
is the greatest node that is in a constraint with 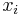 and precedes
and precedes 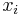 in the ordering.
in the ordering.
Decomposition methods for arbitrary problems
The following methods can be used for translating an arbitrary constraint satisfaction problem, either binary or otherwise. Since they can also be used on binary problems, they can also be used on the result of making constraints binary, either by translating to the dual problem or by using hidden variables.
Some of these methods associate constraints with nodes of the tree, and define width taking into account the number of constraints associated with nodes. This may reduce the width of some problems. For example, a decomposition in which ten variables are associated with each node has width ten; however, if each of these sets of ten variables is the scope of a constraint, each node can be associated that constraint instead, resulting in width one.
Biconnected components
The biconnected decomposition of an arbitrary constraint satisfaction problem is the biconnected decomposition of its primal graph. Every constraint can be enforced on a node of the tree because each constraint creates a clique on its variables on the primal graph, and a clique is either a biconnected component or a subset of a biconnected component.
Tree decomposition
A tree decomposition of an arbitrary constraint satisfaction problem is a tree decomposition of its primal graph. Every constraint can be enforced on a node of the tree because each constraint creates a clique on its variables on the primal graph and, for every tree decomposition, the variables of a clique are completely contained in the variables of some node.
Cycle hypercutset
This is the same mathod of cycle cutset using the definition of cutset for hypergraphs: a cycle hypercutset of a hypergraph is a set of edges (rather than vertices) that makes the hypergraph acyclic when all their vertices are removed. A decomposition can be obtained by grouping all variables of a hypercutset in a single one. This leads to a tree whose nodes are sets of hyperedges. The width of such a decomposition is the maximal size of the sets associated with nodes, which is one if the original problem is acyclic and the size of its minimal hypercutset otherwise. The width of a problem is the minimal width of its decompositions.
Hinge decomposition
An hinge is a subset of nodes of hypergraph having some properties defined below. An hinge decomposition is based on the sets of variables that are minimal hinges of the hypergraph whose nodes are the variables of the constraint satisfaction problem and whose hyperedges are the scopes of its constraints.
The definition of hinge is as follows. Let 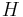 be a set of hyperedges. A path w.r.t.
be a set of hyperedges. A path w.r.t. 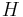 is a sequence of edges such that the intersection of each one with the next one is non-empty and not contained in the nodes of
is a sequence of edges such that the intersection of each one with the next one is non-empty and not contained in the nodes of 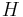 . A set of edges is connected w.r.t.
. A set of edges is connected w.r.t. 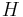 if, for each pair of its edges, there is a path w.r.t.
if, for each pair of its edges, there is a path w.r.t. 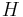 of which the two nodes are the first and the last edge. A connected component w.r.t.
of which the two nodes are the first and the last edge. A connected component w.r.t. 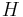 is a maximal set of connected edges.
is a maximal set of connected edges.
Hinges are defined for reduced hypergraphs, which are hypergraphs where no hyperedge is contained in another. A set of at least two edges 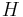 is a hinge if, for every connected component
is a hinge if, for every connected component 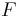 w.r.t.
w.r.t. 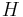 , all nodes in
, all nodes in 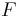 that are also in
that are also in 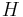 are all contained in a single edge of
are all contained in a single edge of 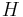 .
.
An hinge decomposition is based on the correspondence between constraint satisfaction problems and hypergraphs. The hypergraph associated with a problem has the variables of the problem as nodes are the scopes of the constraints as hyperedges. An hinge decomposition of a constraint satisfaction problem is a tree whose nodes are some minimal hinges of the hypergraph associated to the problem and such that some other conditions are met. By the correspondence of problems with hypergraphs, a hinge is a set of scopes of constraints, and can therefore be considered as a set of constraints. The additional conditions of the definition of a hinge decomposition are three, of which the first two ensure equivalence of the original problem with the new one. The two conditions for equivalence are: the scope of each constraint is contained in at least one node of the tree, and the subtree induced by a variable of the original problem is connected. The additional condition is that, if two nodes are joined, then they share exactly one constraint, and the scope of this constraint contains all variables shared by the two nodes.
The maximal number of constraints of a node is the same for all hinge decompositions of the same problem. This number is called the degree of cyclicity of the problem or its hingewidth.
Tree clustering
Tree clustering or join-tree clustering is based on merging constraints in such a way the resulting problem has a join tree, this join tree is the result of the decomposition.
A join tree of a constraint satisfaction problem is a tree in which each node is associated a constraints (and vice versa) and such that the subtree of nodes whose constraint contains a variable is connected. As a result, producing a join tree can be viewed as a particular form of decomposition, where each node of the tree is associated the scope of a constraint.
Not all constraint satisfaction problems have a join tree. However, problems can be modified to acquire a join tree by merging constraints. Tree clustering is based on the fact that a problem has a join tree if and only if its primal graph is chordal and conformant with the problem, the latter meaning that the variables of every maximal clique of the primal graph are the scope of a constraint and vice versa. Tree clustering modify an arbitrary problem in such a way these two conditions are met. Chordality is enforced by adding new binary constraints. Conformality is obtained by merging constraints.
In particular, chordality is enforced by adding some "fake" binary constraints to the problem. These are binary constraints satisfied by any pair of values, and are used only to add edges to the primal graph of the problem. In particular, chordality is obtained by adding edges producing the induced graph of the primal graph according to an arbitrary ordering. This procedure is correct because the induced graph is always chordal and is obtained adding edges to the original graph.
Conformality requires that the maximal cliques of the primal graph are exactly the scope of the constraints. While the scope of every original constraint is clique on the primal graph, this clique is not necessarily maximal. Moreover, even if it initially was maximal, enforcing chordality may create a larger clique. Conformality is enforced by merging constraints. In particular, for every maximal clique of the graph resulting from enforcing chordality, a new constraint with the clique as scope is created. The satisfying values of this new constraint are the ones satisfying all original constraints whose scope is contained in the clique. By this transformation, every original constraint is "included" in at least one new constraint. Indeed, the scope of every original constraint is a clique of the primal graph. This clique remains a clique even after enforcing chordality, as this process only introduces new edges. As a result, this clique either is maximal or is contained in a maximal clique.
| An example: a binary constraint satisfaction problem (join-tree clustering can also be applied to non-binary constraints.) This graph is not chordal (x3x4x5x6 form a cycle of four nodes having no chord). | The graph is made chordal. The algorithm analyzes the nodes from x6 to x1. The red edge is the only edge added because x6 is the only node having two non-joined parents. It represents a constraint between x4 and x5 that is satisfied by every pair of values. | The maximal cliques of the resulting graph are identified. Join-tree clustering replaces the constraints on {x3, x4, x5, x6} with two equivalent constraints, one on {x3, x4, x5} and one on {x4, x5, x6}. |
This translation requires the maximal cliques of a chordal graph to be identified. However, this can bone easily using the same ordering used for enforcing chordality. Since the parents of each node are all connected to each other, the maximal cliques are composed of a node (the maximal node of the clique in a max-cardinality ordering) and all its parents. As a result, these maximal cliques can be detected by considering each node with its parents.
The problem that results from this process has a join tree, and such a join tree can be obtained by using the same ordering of variables again. Proceeding from the last node to the first, every constraint is connected with the preceding constraint that shares more variables with it. Join-tree clustering can be seen as a decomposition method in which:
- the elements of the cover are the cliques of the graph resulting from enforcing chordality;
- the tree is the join tree;
- every constraint is assigned to all nodes of the tree whose sets of variables contain the scope of the constraint.
The width of a tree-clustering decomposition is the maximal number of variables associated with each node of the tree. The width of a problem is the minimal width of its tree-clustering decompositions.
Hinge/clustering decomposition
The result of hinge decomposition can be further simplified by decomposing each hinge using tree clustering. In other words, once the hinges have been identified, a tree clustering of each of them is produced. In terms of the resulting tree, each node is therefore replaced by a tree.
Query decomposition
Query decomposition associates a set of variables and a set of constraints to each node of a tree; each constraint is associated to some node, and the subtree induced by the nodes associated to a given variable or constraint is connected. More precisely, for each variable, the subtree of nodes associated to this variable or with a constraint having this variable in its scope is connected. The width of a decomposition is the maximal combined number of variables and constraints associated with a node.
Associating constraints with nodes possibly reduces the width of decompositions and of instances. On the other hand, this definition of width still allows problems of fixed width to be solved in polynomial time if the decomposition is given. In this case, the domain of a new variable is obtained by solving a subproblem which can be polynomially large but has a fixed number of constraints. As a result, this domain is guaranteed to be of polynomial size; the constraints of the new problem, being equalities of two domains, are polynomial in size as well.
| A hypergraph representation of a constraint satisfaction problem: the constraints are given names (P, Q, R, S, T), and their scopes are shown (P (a, b, c) means that constraint P is on the variables {a, b, c} | A query decomposition of the problem. Nodes may contain variables, constraints, or both. Although to the rightmost node are associated a total of five variables (i.e. a,b,c,d,e among the two constraints), this is a decomposition of width 3 because no node contains more than three constraints and isolated variables (there is another decomposition of width 2 and it is possible to show that this decomposition of width 2 is the minimum width of this hypergraph). |
A pure query decomposition is a query decomposion in which nodes are only associated to constraints. From a query decomposition of a given width one can build in logarithmic space a pure query decomposition of the same width. This is obtained by replacing the variables of a node that are not in the constraints of the node with some constraints that contain these variables.
A drawback of this decomposition method is that checking whether an instance has a fixed width is in general NP-complete; this has been proved to be the case with width 4
Hypertree decomposition
A hypertree decomposition associates a set of variables and a set of constraints to each node of a tree. It extends query decomposition by allowing the constraints of a node to contain variables that are not used when creating the domain of the new variable associated with the node. Beside the common conditions for a decomposition method (the scope of each constraint is in at least a set of variables associated with a node and the subtree induced by an original variable is connected), the following two conditions are required to hold:
- each original variable in a node is in the scope of at least one constraint associated with the node;
- the variables of the constraints of a node that are not variables of the node do not occur in the subtree rooted at the node.
The width of a tree decomposition is the maximal number of constraints associated with each node. If this width is bounded by a constant, a problem equivalent to the original one can be built in polynomial time. The variables that are not associated to a node but are in the scope of the constraints of the node are "projected out" when building this instance. This can be done by first projecting the constraints over the variables of the node and then finding all solutions to this subproblem, or by first solving the subproblem with all constraints and then removing the extra variables.
The two requirements above are not necessary to guarantee the equivalence of the original and new problem. They are needed to guarantee that problems of bounded width can be solved in polynomial time.
The possibility of associating a constraint with a node while some of its variables are not effectively associated with the node may produce a width that is less than query width. For example, if a node is associated to 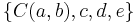 in a query decomposition, and a constraint
in a query decomposition, and a constraint 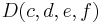 exists, a hypertree decomposition can associate the same node with constraints
exists, a hypertree decomposition can associate the same node with constraints 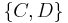 and variables
and variables 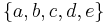 . Since only constraints are computed when checking width, this node has width two. The same node has width four when using query decomposition (one constraint and three variables). This width reduction is possible if two or more variables can be replaced with a single constraint, even if this constraint contains a variable that is not associated with the node.
. Since only constraints are computed when checking width, this node has width two. The same node has width four when using query decomposition (one constraint and three variables). This width reduction is possible if two or more variables can be replaced with a single constraint, even if this constraint contains a variable that is not associated with the node.
Generalized hypertree decomposition
Generalized hypertree decompositions are defined like hypertree decompositions, but the last requirement is dropped; this is the condition "the variables of the constraints of a node that are not variables of the node do not occur in the subtree rooted at the node". A problem can be clearly solved in polynomial time if a fixed-width decomposition of it is given. However, the restriction to a fixed width is not known to being tractable, as the complexity of finding a decomposition of fixed width even if one is known to exist is not known, as of 2001[update].
Comparison
The width of instances is a form of efficiency of decomposition methods. Indeed, given that problems can be solved from decompositions of fixed width, the less the width according to a decomposition, the more the instances that can be solved efficiently using that decomposition.
Some decompositions use the number of variables of a node (or a similar amount) as the width. Others do not: cycle hypercutset, hinge decomposition, query decomposition, hypertree decomposition, and generalized hypertree decomposition associate constraints (or their scopes in form of hyperedges) with nodes, and include the number of constraints associated to a node in the width. This can be a significant save in terms of width. Indeed, problems with a single constraint on  variables can only be decomposed in a tree with a single node. This node can be associated with the
variables can only be decomposed in a tree with a single node. This node can be associated with the  variables or with the single constraint. Counting the number of variables leads to width
variables or with the single constraint. Counting the number of variables leads to width  , while counting the number of constraints leads to width
, while counting the number of constraints leads to width 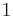 .
.
The comparison between all other decomposition methods is based on generalization and beating. Generalization means that every problem having width  according to a method has width bounded by
according to a method has width bounded by 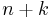 for a fixed
for a fixed 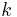 . Beating means that there are classes of problems that have fixed width according to a decomposition method but not according to another. The following are the results for arbitrary problems, where query decomposition is not considered:
. Beating means that there are classes of problems that have fixed width according to a decomposition method but not according to another. The following are the results for arbitrary problems, where query decomposition is not considered:
- hypertree decomposition generalizes and beats all other methods
- hinge decomposition enhanced with tree clustering generalizes and beats both hinge decomposition and tree clustering
- tree clustering is equivalent to tree decomposition (on the primal graph)
- both hinge decomposition and tree clustering generalize and beat biconnected components
- cycle cutset (on the primal graph) is generalized and beaten by both cycle hypercutset and tree clustering
It can also be shown that the tree clustering width is equal to the induced width of the problem plus one. The algorithm of adaptive consistency, which is polynomial for problem of fixed induced width, turns problems into equivalent ones in the same way as the first step of tree clustering.
Solving from a decomposition
Given the tree of a decomposition, solving can be done by constructing the binary tree-like problem as described above, and solving it. This is a polynomial-time problem, as it can be solved in polynomial time using, for example, an algorithm for enforcing directional arc consistency.
A specialized algorithm for the case of binary acyclic problems that result from a decomposition is described as follows. It works by creating constraints that are passed along the edges of the tree, from the leaves to the root and back. The constraint passed along an edge "summarizes" the effects of all constraints of the part of the graph on one side of the edge to the other one.
In a tree, every edge breaks the graph in two parts. The constraint passed along an edge tells how the part of the originating end of the edge affects the variables of the destination node. In other words, a constraint passed from node 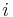 to node
to node 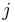 tells how the nodes "on the side of
tells how the nodes "on the side of 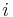 " constrain the variables of node
" constrain the variables of node 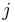 .
.
If the variables of these two nodes are 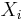 and
and 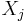 , the nodes on the size of
, the nodes on the size of 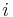 do not affect all variables
do not affect all variables 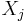 but only the shared variables
but only the shared variables 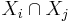 . As a result, the influence on
. As a result, the influence on 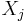 of the nodes on the side of
of the nodes on the side of 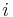 can be represented as a constraint on variables
can be represented as a constraint on variables 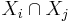 . Such a constraint can be seen as a "summary" of how a set of nodes affects another node.
. Such a constraint can be seen as a "summary" of how a set of nodes affects another node.
The algorithm proceeds from the leaves of the tree. In each node, the summaries of its children (if any) are collected. These summary and the constraint of the node are used to generate the summary of the node for its parent. When the root is reached, the process is inverted: the summary of each node for each child is generated and sent it. When all leaves are reached, the algorithm stops.
| A decomposition tree with associated constraints. All variables have domain {0,..,10} in this example. | The leftmost node contains the constraint a<b and shares the variable b with its parent. These constraint allow b only to take values greater than or equal to 1. This constraint b>0 is sent to its parent. | The left child of the root receives the constraint b>0 and combines it with its constraint b<c. It shares c with its parent, and the two constraints enforce c>1. This constraint is sent to its parent. | When the root has received constraints for all its children, it combines them and sends constraints back to them. The process ends when all leaves are reached. At this point, the allowed values of variables are explicit. |
The set of variables shared between two nodes is called their separator. Since the separator is the intersection between two sets associated with nodes, its size cannot be larger than the induced width of the graph.
While the width of the graph affects the time required for solving the subproblems in each node, the size of the separator affects the size of the constraints that are passed between nodes. Indeed, these constraints have the separators as scope. As a result, a constraint over a separator of size  may require size
may require size 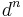 to be stored, if all variables have domain of size
to be stored, if all variables have domain of size 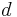 .
.
Memory/time tradeoff
The algorithm for solving a problem from a decomposition tree includes two operations: solving a subproblem relative to a node and creating the constraint relative to the shared variables (the separator) between two nodes. Different strategies can be used for these two operations. In particular, creating the constraints on separators can be done using variable elimination, which is a form of inference, while subproblems can be solved by search (backtracking, etc.)
A problem with this algorithm is that the constraints passed between nodes can be of size exponential in the size of the separator. The memory required for storing these constraints can be decreased by using a tree decomposition with small separators. Such decomposition trees may however have width (number of nodes in each node) larger than optimal.
For a given decomposition tree, a fixed maximal allowed separator size can be enforced by joining all pairs of nodes whose separator is larger than this size. Merging two nodes usually produces a node with an associated set of variables larger than those of the two nodes. This may increase the width of the tree. However, this merging does not change the separators of the tree other than removing the separator between the two merged nodes.
The latter is a consequence of acyclicity: two joined nodes cannot be joined to the same other node. If 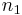 and
and 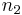 are two nodes to be merged and
are two nodes to be merged and 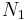 and
and 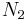 are the sets of nodes joined to them, then
are the sets of nodes joined to them, then 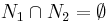 , as otherwise there would be cycle in the tree. As a result, the node obtained by merging
, as otherwise there would be cycle in the tree. As a result, the node obtained by merging 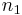 and
and 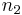 will be joined to each of the nodes of
will be joined to each of the nodes of 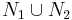 . As a result, the separators of this merged node are exactly the separators of the two original nodes.
. As a result, the separators of this merged node are exactly the separators of the two original nodes.
As a result, merging a pair of nodes joined by a separator does not change the other separators. As a result, a fixed maximal separator size can be enforced by first calculating all separator sizes and then iteratively merging any pair of nodes having a separator larger than a given amount, and the size of the separators do not need to be recalculated during execution.
Structural restrictions
Bounding the width of a decomposition method by a constant creates a structural restriction, that is, it limits the possible scopes of constraints, but not their relations. The complementary way for obtaining tractable subclasses of constraint satisfaction is by placing restriction over the relations of constraints; these are called relational restriction, and the set of allowed relations is called constraint language.
If solving problems having a decomposition width bounded by a constant is in P, the decomposition leads to a tractable structural restriction. As explained above, tractability requires that two conditions are met. First, if the problem has width bounded by a constant then a decomposition of bounded width can be found in polynomial time. Second, the problem obtained by converting the original problem according to the decomposition is not superpolynomially larger than the original problem, if the decomposition has fixed width.
While most tractable structural restrictions derive from fixing the width of a decomposition method, others have been developed. Some can be reformulated in terms of decomposition methods: for example, the restriction to binary acyclic problem can be reformulated as that of problem of treewidth 1; the restriction of induced width (which is not defined in terms of a decomposition) can be reformulated as tree clustering.
An early structural restriction (that later evolved into that based on induced width) is based on the width of the primal graph of the problem. Given an ordering of the nodes of the graph, the width of a node is the number of nodes that join it and precede it in the order. However, restricting only the width does not lead to a tractable restriction: even restricting this width to 4, establishing satisfiability remains NP-complete. Tractability is obtained by restricting the relations; in particular, if a problem has width 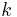 and is strongly
and is strongly 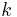 -consistent, it is efficiently solvable. This is a restriction that is neither structural nor relational, as it depends on both the scopes and the relations of the constraints.
-consistent, it is efficiently solvable. This is a restriction that is neither structural nor relational, as it depends on both the scopes and the relations of the constraints.
Online Resources
Here are some links to online resources for tree/hypertree decomposition in general.
- Treewidthlib: A benchmark for algorithms for Treewidth and related graph problems
- A C++ implementation used in the paper "A complete Anytime Algorithm for Treewidth, Vibhav Gogate and Rina Dechter, UAI 2004." The link is to the author homepage, where both LINUX source and Windows executable is distributed.
- An implementation of Hypertree Decomposition, using several heuristics.
- Toolbar tool has implementation of some tree decomposition heuristics
- TreeD Library: has source code of some decomposition methods
References
- Dechter, Rina (2003). Constraint Processing. Morgan Kaufmann. http://www.ics.uci.edu/~dechter/books/index.html. ISBN 1-55860-890-7
- Downey, Rod; Michael Fellows (1997). Parameterized complexity. Springer. http://www.springer.com/sgw/cda/frontpage/0,11855,5-0-22-1519914-0,00.html?referer=www.springer.de%2Fcgi-bin%2Fsearch_book.pl%3Fisbn%3D0-387-94883-X. ISBN 0-387-94883-X
- Gottlob, Georg; Nicola Leone, Francesco Scarcello (2001). "Hypertree Decompositions: A Survey". MFCS 2001. pp. 37–57. http://www.springerlink.com/(rqc54x55rqwetq55eco03ymp)/app/home/contribution.asp?referrer=parent&backto=issue,5,61;journal,1765,3346;linkingpublicationresults,1:105633,1.
- Gottlob, Georg; Nicola Leone, Francesco Scarcello (2000). "A comparison of structural CSP decomposition methods". Artificial Intelligence 124 (2): 243–282. doi:10.1016/S0004-3702(00)00078-3.